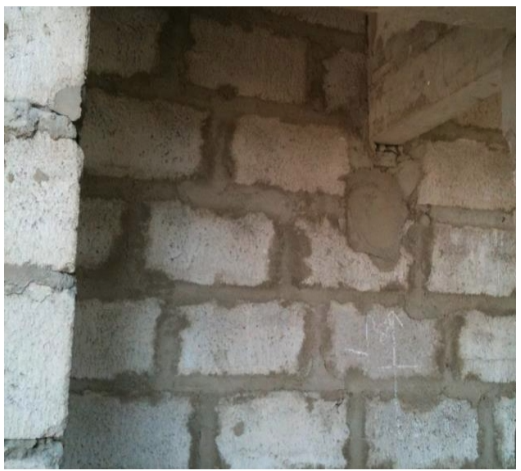
Generally, block work is done above the DPC level. It’s made of stone units with mortar. Cement-sand blocks are cast in a 1:6 mixture and can be built in a 1:5 cement-sand mixture.
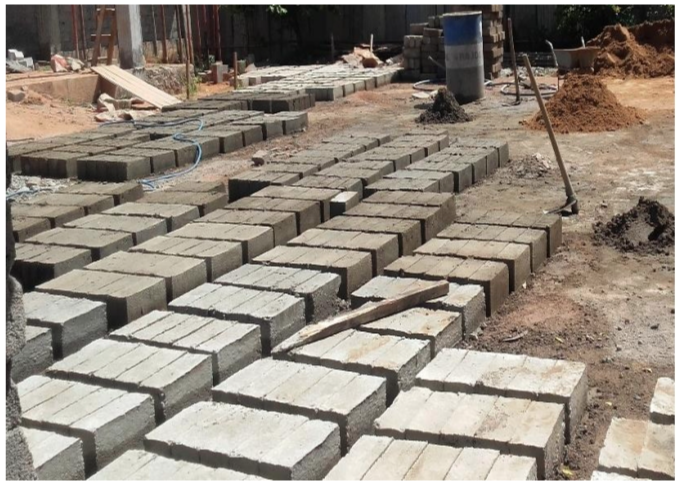

SLS-certified cement (SLS 107) and river sand are widely used for block casting. The expiry date of the cement and the quality of the river sand should be checked before the preparation of the mixture. After the block casting work is finished the blocks should be put into the water basin for curing purposes to gain a particular strength. After 7 days (minimum 3 days) the blocks are taken outside from the water basin. Then the blocks are cleaned, dried, and stacked respectively.
At first, setting out is done at the area where the block work would be done. The area and the blocks should be wetted before the masonry work is carried out. Continuous vertical joints should be avoided and the verticality of the stones should be checked for each layer by using the plumb-bob when the stone masonry is being carried out.
Checklist for block work
- Quality of materials ( Block & sands)
- Size
- Crushing strength
- Mix of water
- Water/cement ratio
- Type of bond
- Expansion joints if required
- Soaking immediately before using
- Horizontal & Vertical level
- Construction height
Wall Construction
All blocks shall be sound, free from cracks, broken edges, honeycombing, and other defects that would interfere with the proper placing of blocks or impair the strength or performance of construction.
Method of wall construction using block
- The slab area on which the wall is built should be chipped, (if smooth) cleaned and wetted before the work begins.
- A layer of cement grout is then applied on the slab area as well as on the sides of columns, which, would be bound by the wall to ensure a sound bonding with the blockwork.
- The verticality of the wall is checked with the plumb bob, and generally, two blocks of a particular side are checked for verticality and the balance is adjusted according to that. In a stretcher course block work, the two blocks are laid by setting the outer edges at the exact spacing and leveling both sides. A header course is leveled only at one side of the
wall. - The soaking process of blocks is very important otherwise the water in the mortar is absorbed by the block