The roof is an essential part of every building. Technically speaking, the roof refers to the framework of either timber, steel, or concrete on which a covering of thatch, tile, corrugated asbestos, etc is placed. The main function of a roof is to protect from weather such as rain, wind, sun, snow and dust.
Functions of Roof
- To keep out rain, wind, snow, sun and dust.
- To prevent excessive heat loss in cold weather
- To keep the interior of the building cool in hot weather
- Designed to accommodate all stresses encountered.
- Designed to accept movement due to changes in temperature and moisture content.
- To accommodate services
Functional Requirements of Roof
- weather resistant
- Strength and Stability provision.
- Thermal insulation
- Sound insulation
- Fire resistant
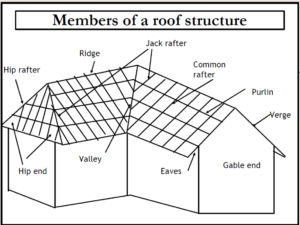
- Ridge: This is the pitching plate for the rafters which are nailed to each other through a ridge board. The depth of the ridge board is governed by the pitch of the roof.
- Common rafters: The main load-bearing members of a roof, span between a wall plate at eaves and the ridge.
- Jack rafters: These fulfil the same function as common rafters, but span from ridge to valley or from hip rafter to wall plate.
- Hip rafters: Similar to the ridge but forming the spine of an external angle and similar to a rafter spanning from ridge to wall plate.
- Valley rafter: These provide the bearing and fixing medium for various roof members and distribute the loads evenly over the supporting walls.
- Purlin: These act as a beam and reduce the span of the rafters. These are used to support the roof covering.
- Verge: The edge of a sloping roof which overhangs a gable.
Terms associated with a Roof
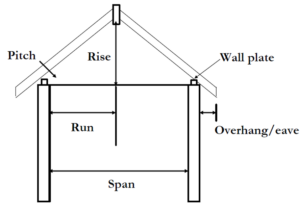
- Rise: This is the vertical distance from the wall plate to the ridge.
- Span: This is the distance from the inside of one wall across to the wall.
- Run: This is half of the span.
- Wall plates: these receive the feet of the common rafters and distribute their loads evenly over the wall.
- Slope: This is given in degrees and refers to the inclination of the roof to the horizontal.
- Pitch: This refers to the ratio of the rise to the run.
- Pitch = Rise/Run
- The pitch is generally expressed in degrees.
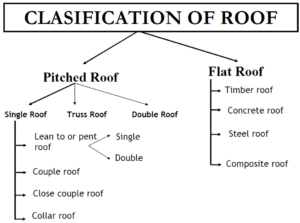
Factors determine the choice 0f roof
- Type of building: whether a domestic, commercial, industrial or social building
- Size and plan or shape of the building
- Span to be covered
- Foundation conditions
- Nature and magnitude of the loads that may be imposed on the roof, including the suspension of machinery
- Lighting requirements and accommodation for services
- Possibility of future alteration
- Speed of construction or erection
- Appearance or aesthetic consideration
- Cost of construction
- Ease of effective repairs