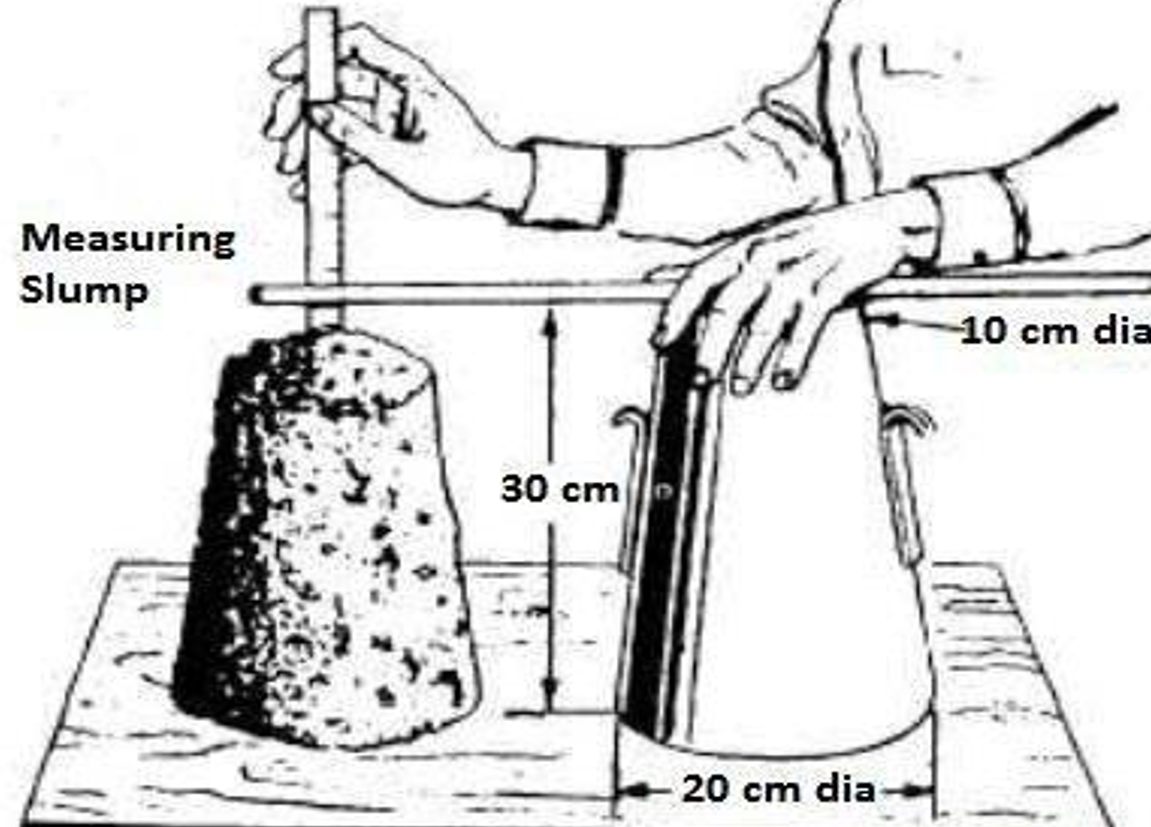
The concrete slump test or slump cone test determines the workability or consistency of the concrete mix prepared at the laboratory or the construction site during the progress of the work. Concrete slump test is carried out from batch to batch to check the uniform quality of concrete during construction. It is the simplest workability test for concrete, involves low cost and provides immediate results.
Generally, the concrete slump value is used to find the workability, which indicates the water-cement ratio. However, various factors, including the properties of materials, mixing methods, dosage, admixtures, etc., also affect the concrete slump value.
Factors which influence the concrete slump test
- Material properties include chemistry, fineness, particle size distribution, moisture content, and temperature of cementitious materials. Size, texture, combined grading, cleanliness and moisture content of the aggregates,
- Chemical admixtures dosage, type, combination, interaction, sequence of addition and its effectiveness,
- Air content of concrete
- Concrete batching, mixing and transporting methods and equipment
- Temperature of the concrete
- Sampling of concrete, slump-testing technique and the condition of test equipment
- The amount of free water in the concrete
- Time since mixing of concrete at the time of testing.
Equipment Required for Concrete Slump Test
- Slump cone
- Nonporous base plate
- Measuring scale
- Tamping rod. – The tamping rod is made of steel 16 mm in diameter and 60cm long and rounded at one end.
- The mould for the test is in the form of the frustum of a cone having a height of 30 cm, a bottom diameter of 20 cm and a top diameter of 10 cm.
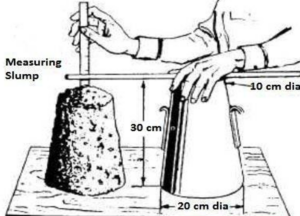
Procedure for Concrete Slump Cone Test
- Clean the internal surface of the mould and apply oil.
- Place the mould on a smooth horizontal non-porous base plate.
- Fill the mould with the prepared concrete mix in 4 approximately equal layers.
- Tamp each layer with 25 strokes of the rounded end of the tamping rod in a uniform manner over the cross-section of the mould. For the subsequent layers, the tamping should penetrate the underlying layer.
- Remove the excess concrete and level the surface with a trowel.
- Clean away the mortar or water leaked out between the mould and the base plate.
- Raise the mould from the concrete immediately and slowly in the vertical direction.
- Measure the slump as the difference between the height of the mould and the height point of the specimen being tested.
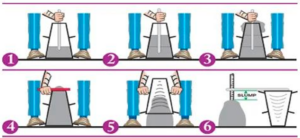
Slump Value Observation
The slump (Vertical settlement) measured shall be recorded in terms of millimetres of subsidence of the specimen during the test.
Results of Slump Test on Concrete
Slump for the given sample= _____mm
When the slump test is carried out, the following are the shape of the concrete slump that can be observed:
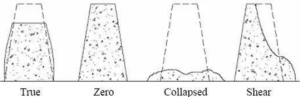
- True Slump– True slump is the only slump that can be measured in the test. The measurement is taken between the top of the cone and the top of the concrete after the cone has been removed as shown in figure-1.
- Zero Slump– Zero slump is the indication of a very low water-cement ratio, which results in dry mixes. This type of concrete is generally used for road construction.
- Collapsed Slump– This is an indication that the water-cement ratio is too high, i.e. concrete mix is too wet or it is a high workability mix, for which a slump test is not appropriate.
- Shear Slump– The shear slump indicates that the result is incomplete, and concrete to be retested.