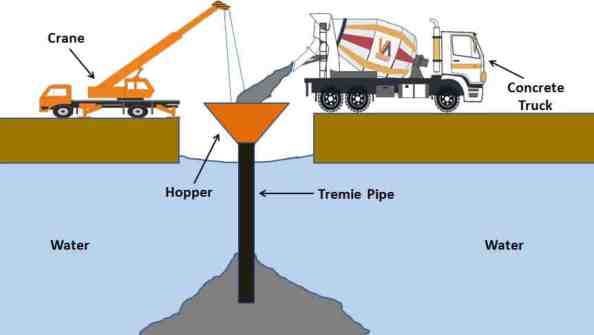
Underwater concreting is a specialized construction technique that involves placing and curing concrete underwater. It’s used to build structures like bridges, dams, and offshore platforms. Concrete placement underwater poses several problems, as concrete cannot be compacted and concrete may get mixed with water. Whenever possible underwater concreting is to be avoided. To overcome the problems mentioned above, concrete must be self-compacting and wet enough to flow under its weight.
Characteristics of underwater concrete
- highly flowable concrete that can flow and spread only under its self-weight.
- can achieve good compaction without vibration.
- has high strength.
- sets and hardens rapidly.
- has a low tendency to segregation and bleeding.
The major problem in underwater concreting is the washing out of fine materials.
It can be controlled by,
- Minimizing disturbance of water in the vicinity
- Using anti-wash-out admixtures
In the underwater concreting process, the concrete placed should be self-compacting and remain plastic for sufficient time to carry out the operation.
Techniques used for placing concrete underwater
- Tremie method
- Hydrovalve method
- Toggle bags method
- Pumping technique
- Pneumatic valve method
- Tilting pallet barge method
- Grouting of preplaced aggregate concrete
- Pre-packed or grouted concrete
- The bucket or skip method